In 2022, Nigeria’s UNESCO World Heritage Sites witnessed a notable increase in international tourist arrivals, reflecting a growing global interest in the country’s rich cultural and natural heritage. This uptick highlights the potential of heritage tourism as a significant contributor to Nigeria’s economy and cultural diplomacy.
Key UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Nigeria
Nigeria is home to several UNESCO World Heritage Sites, each offering unique insights into the nation’s history and culture:
-
Osun-Osogbo Sacred Grove (Osun State): This sacred forest, dedicated to the goddess Osun, is renowned for its annual Osun-Osogbo Festival, which attracts thousands of worshippers and tourists from around the world. The festival, celebrated every August, has become a major cultural event, drawing significant international attention.
-
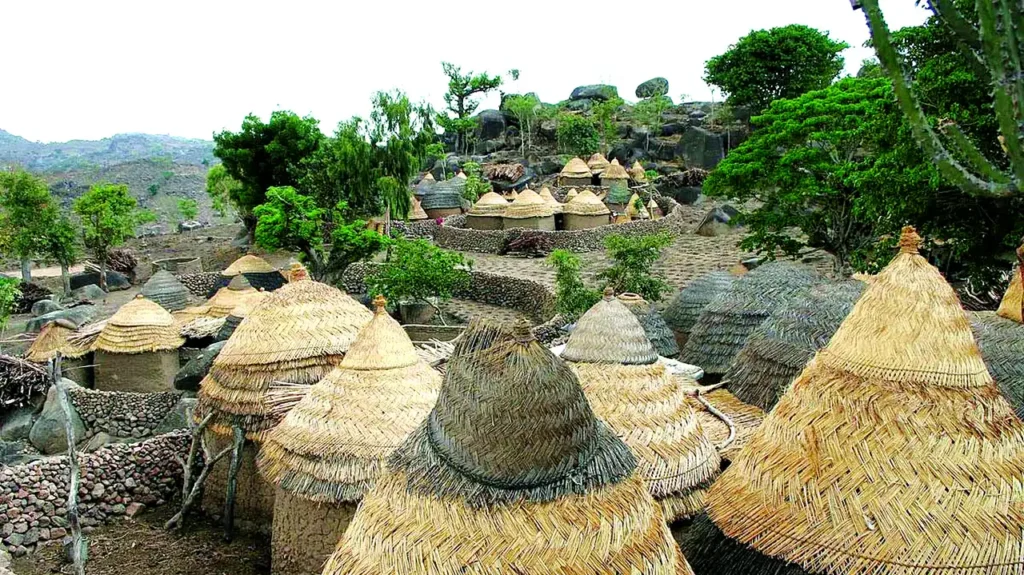
Sukur Cultural Landscape (Adamawa State): Located in the Mandara Mountains, Sukur is recognized for its terraced fields and traditional palace, offering a glimpse into the indigenous culture and architecture of the region.
-
Oke-Idanre Hill (Ondo State): This site features a series of hills with ancient settlements, shrines, and festivals that continue to attract visitors interested in Nigeria’s pre-colonial history.
-
Ogbunike Caves (Anambra State): A network of caves with historical significance, Ogbunike Caves have become a point of interest for tourists exploring Nigeria’s natural wonders.
-
Oban Hills (Cross River State): Part of the Cross River National Park, Oban Hills is known for its biodiversity and is increasingly recognized by eco-tourists.

Tourism Growth and Economic Impact
According to the Nigerian Ministry of Tourism, the country welcomed over 1.2 million international visitors in 2023, marking a significant increase from previous years. This growth is attributed to various factors, including enhanced marketing of heritage sites and improved infrastructure. The tourism sector’s contribution to Nigeria’s GDP has also seen an upward trend, indicating the economic potential of cultural tourism.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the positive growth, Nigeria’s heritage tourism faces challenges such as inadequate infrastructure, security concerns, and the need for sustainable management practices. Addressing these issues through policy reforms and investment in tourism infrastructure can further enhance the sector’s contribution to the economy.
Conclusion
The rise in international tourism to Nigeria’s UNESCO World Heritage Sites in 2022 underscores the country’s rich cultural and natural assets. With continued investment and strategic planning, heritage tourism can play a pivotal role in Nigeria’s economic development and cultural preservation